本人选择了2018spring的课程,因为他免费提供了评分机器,后来得知2021也开放了,决定把其中的Lab尝试一番,听说gitlab就近好评,相当有实力,并借此学习Java的基本知识,请根据pku的cswiki做好评分机器准备,请自行下载IJ IDEA,可以选择破解专业版,感谢伯克利大学和Josh Hug开源如此优质知识
根据前人所说,此课程需要200h,我第一个同学花费了约30到40天暑假时间学完了,估算大概一天5-7h的专精学习时间,现在我在学校,希望from9.18大概50day可以完成😭😭😭😭😭失败了11.7也没看完,都怨那个sb的人工智能相关内容
第一二parts简述了学期任务,评估目标与要求,测评方法等等。看看就好.
Java的基础知识
public class HelloWorld{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("hello world");
}
}public class HelloWorld{
public static void main(String[] args){
int x=0;
while(x<10){
System.put.println(x);
x=x+1;
}
x="horse";
}
}1. Before Java variables can be used, they must be declared.
2. Java variables must have a specific type.
3. Java variable types can never change.
4. Types are verified before the code even runs!!!
public class LargerDemo{
/** Returns the Larger of x and y.*/
public static int larger(int x, int y) {
if (x > y) {
return x;
}
return y;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println(larger(-5, 10));
}
}
/*
1. Functions must be declared as part of a class in Java. A function that is part of a cLass is calLed a "method". So in Java, all functions are methods.
2. To define a function in Java, we use "public static". We will see alternate ways of defining functions Later.
3. ALL parameters of a function must have a decLared type,
and the return value of the function must have a decLared type. Functions in Java return onLy one value!
*/
why在jdk23中要求编译以上文件 C:\Users\eve\IdeaProjects\newprojects\src\Main.java
java: 类 LargerDemo 是公共的, 应在名为 LargerDemo.java 的文件中声明,OK我知道了,只要把文件名修改一下即可

lab1和homework0都很简单。是对Java的简单应用。可能cmd部分很有用,不过你应该在linux部分进行了详细学习,git你也是学习使用过了
发现joshhug.gitbooks.io/hug61b是课程教案一样的东西.
Creating and Defining Classes
我们只在cmd输入ls进入到HelloWorld.java文件中,javac HelloWorld.java即可编译运行,但是得到了class文件,这时我们Java HelloWorld就可以解释运行成功,输出helloworld

public class Dog{
public static void makeNoise(){
System.out.println("Bark!");
}
}
public class DogLauncher{
public static void main(String[] args){
Dog. makeNoise();
}
}我们实从类中例一个对象
public class Dog{
public int weightInPounds;
public /*static*/ void makeNoise(){
if (weightInPounds <10){
System.out. println("yip!");
} else if (weightInPounds < 30){
System.out. println("bark.");
} else{
System.out. println("woooof!");
}
}
}
运行后我们按照编译器信息删除static,然后创建一个d的dog.重复,执行
public class DogLaimcher{
public static void main (String[] args)
Dog d =new Dog();
d.weightInPounds=51;
d.makeNoise();
}
}构造函数:
public Dog(int w){
wewightInPounds=w;
}这样可以Dog d=new Dog(51);d.makeNoise();成功运行
现在阐述为什么去掉static,因为使用了其中的实例变量,与static冲突,这使编译器感到困惑
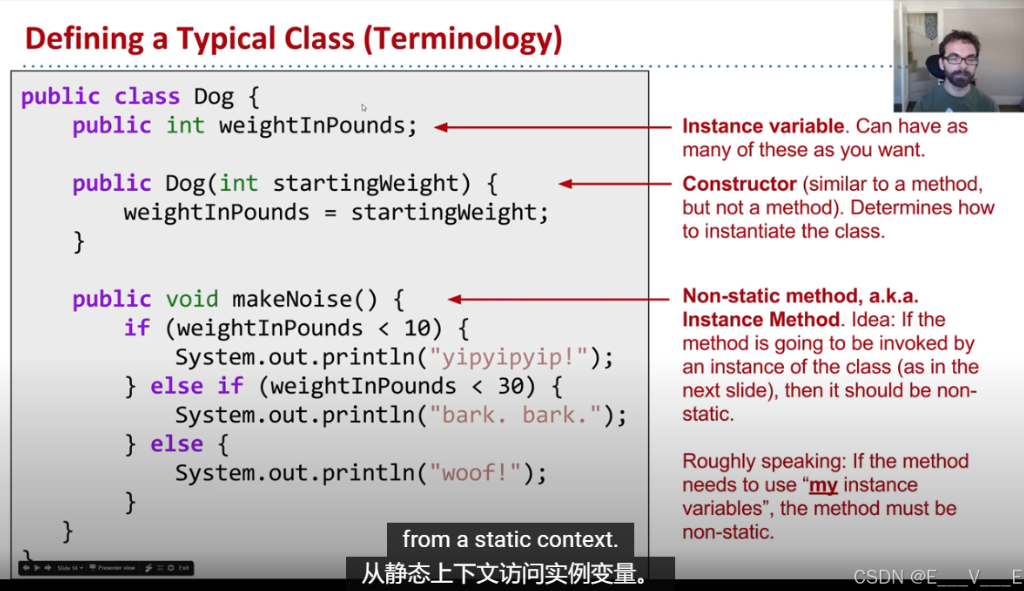
缺少对下面此图片部分笔记
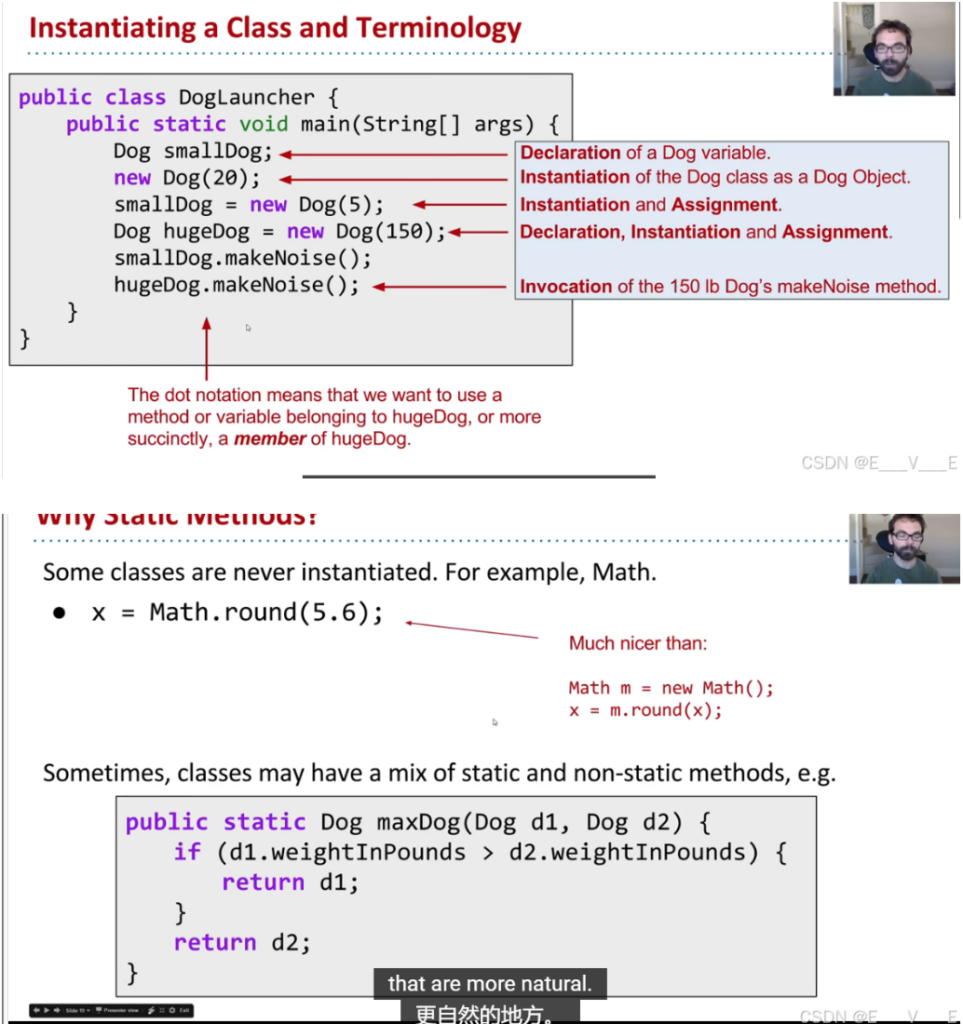
你可以拥有一个静态和非静态的类,把他们混合
public class Dog{
public int weightInPounds;
public static String binomen="Canis familiaris"
/*创建一个适用于所有狗的变量,可以在对象d,d2或者Dog使用*/
public Dog(int w){
weightInPounds=w;
}
public void makeNoise(){
if (weightInPounds 10){
System.out. println("yip!");
}else if (weightInPounds 30){
System.out. println("bark.");
}else{
System.out. println("woooof! ");
}
}
public static Dog maxDog(Dog d1, Dog d2){
if (dl. weightInPounds d2.weightInPounds) {
return d1;
}
return d2;
}
public Dog maxDog(Dog d2){
/*非静态方法,因为是由特定的dog进行判断*/
if (this.weightInPounds>d2.weightInPound){
return this;
}
return d2;
}
}在一个类中定义的变量或方法也称为该类的成员.
使用类名访问静态成员,例如Dog.binomen.
不能使用类名调用非静态成员:Dog.makeNoise
静态方法必须通过特定的实例访问实时变量,例如d1.
比如我们删除这个方法Dog maxDog(Dog d2)编译器报错。对于非静态成员,如果只有一个方法的非静态版,就不能用类名来运行函数;如果有一个静态方法,并且想访问某种实例变量,必须指明是哪个实例(比如里面的this.)
回答以下代码会输出什么?
public class DogLoop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog smallDog = new Dog(5);
Dog mediumDog = new Dog(25);
Dog hugeDog = new Dog(150);
Dog[] manyDogs = new Dog[4];
manyDogs[0] = smallDog;
manyDogs[1] = hugeDog;
manyDogs[2] = new Dog(130);
int i = 0;
while (i < manyDogs.length) {
Dog.maxDog(manyDogs[i], mediumDog).makeNoise();
i = i + 1;
}
}
public static class Dog {
/* Size of the dog in standard dog size units. */
public int size;
/* This is a constructor. It tells us how to construct
* dogs from our ideal notion of dogness. */
public Dog(int s) {
size = s;
}
public void makeNoise() {
if (size < 10) {
System.out.println("hideous yapping");
} else if (size < 30) {
System.out.println("bark!");
} else {
System.out.println("woof!");
}
}
/* Return the larger of dog d1 and dog d2. */
public static Dog maxDog(Dog d1, Dog d2) {
if (d1.size > d2.size) {
return d1;
}
return d2;
}
}
}
这是一个java可视化网站 Java Visualizer (uwaterloo.ca)对以上问题做出回答!
一点扩展在creating and defining classes9/10中0.0-2.20的话
现在要求创建一个程序ArgsSum,打印出命令参数的总和,假设他们是数字
public class ArgsSum {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = args.length;
int i = 0;
int sum = 0;
while (i < N) {
sum = sum + Integer.parseInt(args[i]);/*string to int的方法*/
i = i + 1;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}Libraries库的使用 推荐使用stackoverflow
普林斯顿大学library,请做project0?










Comments NOTHING